S&P 500 slides as tech and AI investment uncertainty mounts
U.S. equities came under broad pressure, with the S&P 500 falling 1.16%, as selling intensified across technology and semiconductor stocks. The decline highlights a shift in market sentiment, as investors move toward a more cautious, defensive stance following a prolonged period of gains. Losses were widespread across the index, reflecting growing concern about high-valuation sectors that have driven much of the market’s recent strength.

Pressure on the S&P 500 was led by weakness in large-cap technology.
Oracle shares have fallen almost 46% since they peaked.
Spending on big tech might slow down.
Uncertainty surrounding AI infrastructure investment
The pressure on the S&P 500 was concentrated in large-cap technology companies, as doubts emerged over the sustainability of spending on artificial intelligence infrastructure. Oracle shares dropped 5.4% after reports that its largest data-center partner, Blue Owl, declined to support the company’s proposed $10 billion data center project. This news raised questions about the pace, scale, and funding of future AI-related investments, prompting investors to reassess expectations across the broader market. Given the heavy weighting of technology stocks in S&P 500, the impact was quickly reflected at the index level. Semiconductor stocks were particularly hard hit, with Nvidia down 3.8%, Broadcom falling 4.5%, and AMD sliding 5.3%, as investors took profits following strong rallies earlier in the year. The pullback reflects a more cautious approach to the sector, with market participants increasingly sensitive to any signs that capital spending on AI and cloud infrastructure could slow, even slightly. After months of strong optimism, high valuations in the semiconductor space left little room for disappointment, making the sector especially vulnerable to negative headlines.
Blue Owl declined to support Oracle
Oracle’s shares have tumbled nearly 46% since peaking in early September, marking a significant reversal after a strong rally earlier in the year. The decline reflects a clear shift in investor sentiment as expectations for Oracle’s role in large-scale AI infrastructure projects are reassessed. Optimism that previously drove the stock higher has been replaced by caution, particularly as questions arise about the scale, timing, and profitability of major investment plans. Much of the recent pressure stems from concerns over the sustainability of heavy capital spending, especially after Blue Owl declined to support Oracle’s proposed $10 billion data center project. This raised doubts about Oracle’s ability to secure long-term funding partners for ambitious expansion plans and highlighted the financial risks tied to large upfront investments. In a climate of elevated interest rates and tighter financing conditions, investors are increasingly sensitive to the balance between growth ambitions and financial discipline. As a result, Oracle has been vulnerable to profit-taking, particularly after its earlier strong performance left valuations stretched. Negative headlines and uncertainty about future AI-related returns have added to the pressure, underscoring how quickly sentiment can shift for companies closely tied to AI investment themes.
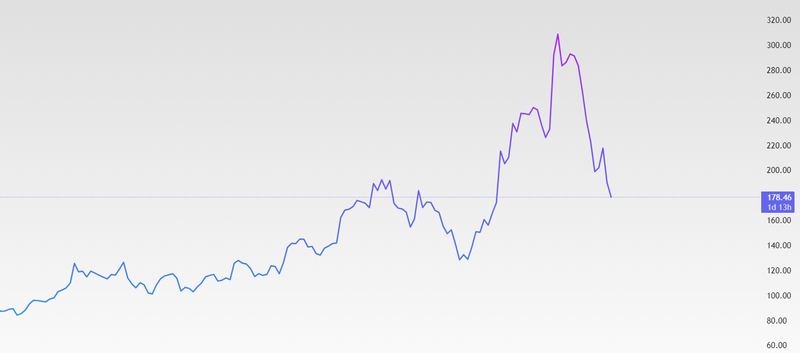
Source: Trading View
Market mood shifts
The recent pullback in U.S. stocks is not limited to tech and semiconductor companies. Broadly, investors are becoming more cautious after a long period of gains. Many are focusing on managing risk and reducing exposure to sectors that have become expensive and rely heavily on continued business spending. This slowdown suggests that the market is beginning to question whether recent optimism is sustainable, especially given that borrowing costs remain high. While there’s no clear sign of a recession, the drop in the S&P 500 highlights how quickly investor confidence can change when the outlook for corporate profits becomes uncertain. In the near term, equity performance is likely to remain sensitive to company updates, investment plans, and any indications that spending on large tech or infrastructure projects might slow, even modestly.