Tesla hits $498 with rising competition and technological ambitions
Tesla’s stock recently reached an all-time high of $498, reflecting investor optimism about its long-term growth potential in autonomous driving, AI, and robotics. While the stock price embodies future optionality, the company faces structural headwinds from slowing EV deliveries, aggressive Chinese competitors, and execution risks in emerging technologies. Tesla’s near-term performance, competitive positioning, and progress in AI-driven initiatives.
Company delivered roughly 1.64 million vehicles, down 16% year-over-year.
Tesla’s historic technological lead is being challenged.
Net income has shrunk 59% year-over-year.
Automotive performance and market pressures
Tesla’s vehicle deliveries in Q4 2025 totaled approximately 1.64 million units, down 16% year-over-year, marking the second consecutive annual decline. Aging models like the Model 3 and Model Y still account for most volume, while Chinese competitors such as BYD, XPeng, and NIO continue to expand aggressively, offering newer models and advanced software features. BYD alone surpassed Tesla in global EV deliveries, delivering over 2.25 million vehicles in 2025, signaling a structural shift in global EV leadership.
Looking forward, Tesla’s near-term automotive growth appears constrained. With U.S. EV incentives declining and global competition increasing, vehicle deliveries may continue to plateau unless Tesla introduces refreshed models or expands into untapped markets. If the company can accelerate production of next-generation models and maintain pricing power, EV revenue could stabilize in 2026. Conversely, failure to innovate or defend share could result in further volume erosion, putting pressure on overall earnings.
Competition and strategic challenges
Tesla faces growing competition not only in volume but also in technology. Chinese EV makers are advancing rapidly in AI, autonomous features, and cost efficiency, challenging Tesla’s long-standing first-mover advantage. Even as Tesla retains a premium brand position in North America, competitors are gaining share in China and Europe, creating pressure on margins and highlighting the difficulty of maintaining global dominance without continued innovation.
Predictively, Tesla’s ability to retain market share will hinge on how effectively it leverages its technology lead in autonomy and software. If Tesla successfully commercializes FSD subscriptions, robotaxi services, or other software-driven offerings, it could offset competitive pressures and stabilize revenue. However, sustained market share losses in key regions or price competition could compress margins further, making profitability a central determinant of stock performance in 2026.
Financial performance and profitability outlook
Tesla’s latest financials show significant pressure on earnings. Net income has shrunk 59% year-over-year and 13% quarter-over-quarter, while net margins have contracted by a similar magnitude. Operating income is down 40% YoY and 19% QoQ, and the operating margin fell 40% YoY and 23% from the previous quarter. These declines reflect rising costs, slowing EV volume, and heavy investments in AI, autonomy, and robotics initiatives.
Looking forward, margins and profitability will likely determine whether the stock can sustain its high value. If Tesla manages to control costs, optimize production, and monetize FSD and robotaxi offerings, operating margins could gradually recover, supporting further upside in the stock. Conversely, continued margin erosion or delays in software and robotics revenue could trigger downward pressure on shares. Analysts and investors will be watching closely for early indicators of margin stabilization or expansion, which could signal whether Tesla’s current valuation is justified or overly optimistic.
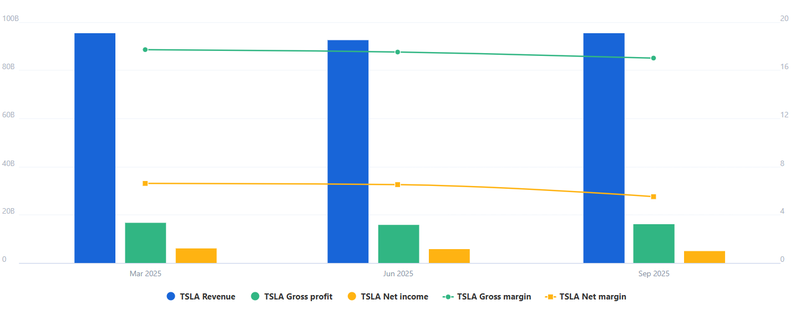
Source: FullRatio