China Q4 2025 Outlook

China’s recovery built on policy support and tech edge
China enters the Q4 with a fragile but stabilising outlook. Inflation remains subdued, but GDP growth and services are showing resilience. Policy support and strength in critical minerals and technology are helping to steady markets, suggesting the economy may be shifting towards gradual recovery.
CPI weakness and emerging growth
China’s economy remains fragile, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) standing out as the weakest indicator, reflecting soft domestic demand and periods of deflation. In August, China’s CPI fell 0.4% from a year earlier, showing continued weakness in prices.
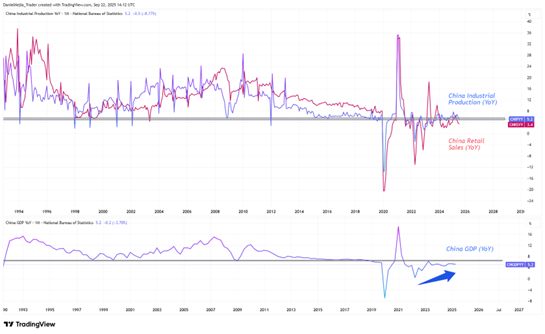
Industrial production and retail sales are growing but remain subdued compared with historical norms. Output rose 5.2% and retail sales 3.4% year-on-year in August, both well below the long-term averages of 12% and 13.5% seen from 1993 to 2019. Since 2020, growth has slowed to averages of 5.5% for industry and 4% for retail.
However, signs of recovery have been visible since June 2022, with year-on-year growth in real GDP moving steadily higher.
Historically, between 1993 and 2019 China’s economy grew at an average rate of 9.4%, compared with an average of 4.9% for 2020 to 2025.
In Q2 2025, GDP expanded by 5.2% year-on-year, ahead of both its recent average and the global average of 2.9% (World Bank). Sustaining growth above the global pace is difficult for a large, mature economy, yet China remains the world’s second-largest with a nominal GDP of $19.23 trillion, compared with $30.51 trillion in the United States.
Another sign of recovery comes from the NBS Non-Manufacturing PMI, which has stayed in expansion territory throughout every month of 2025, averaging 50.37 year-to-date.
Stimulus through spending and easing
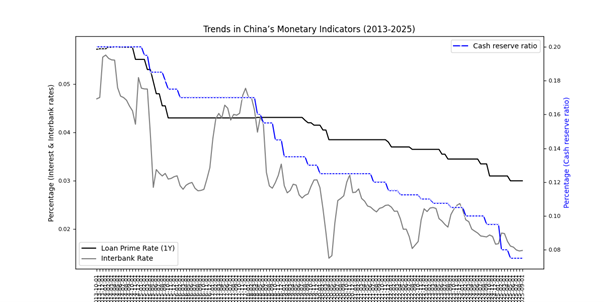
In response to prolonged economic weakness, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) has steadily eased policy since 2013.
The one-year Loan Prime Rate (LPR) has been reduced from 5.72% to 3.0%, including a 10-basis-point cut in May 2025. The five-year LPR, the main benchmark for mortgages, now stands at 3.5%.
Over the same period, the Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR) has been lowered from 20% to 7.5%, with the most recent 50-basis-point reduction also announced in May 2025. As a result, interbank rates have declined in line with the LPR, falling from 4.7% to 1.56%.
The government has adopted a more expansionary fiscal policy to counter weak demand. By the end of 2024, the budget deficit had risen to 6.5% of GDP. In 2025, stimulus has been sizeable but targeted, with measures focused on supporting consumption and financing public works.
Local governments have accelerated infrastructure projects in transport, energy and technology, although fixed-asset investment has grown more slowly than expected. Additional support has gone to real estate, defence and social spending.
Stocks driven by minerals and tech
With policy support and early signs of recovery in place, China’s main equity indices have recorded strong gains. Year-to-date, Hang Seng Index futures, which track the 50 largest companies on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, are up about 34%.
CSI 300 Index futures, which cover the 300 largest and most liquid companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges, have risen about 18%. FTSE China A50 Index futures, tracking the 50 biggest companies by market capitalisation on the same exchanges, are up roughly 15%. Overall performance has been strong, outpacing major global benchmarks, including US and European markets that have historically led.
Two further factors likely supporting Chinese equities are the country’s comparative and competitive advantages. According to the International Energy Agency’s Global Critical Minerals Outlook 2025, China leads the refining of 19 out of 20 strategic minerals for the energy transition, with an average global market share of about 70%.
The US Geological Survey’s Mineral Commodity Summaries 2025 also shows that China was the top producer of 30 out of 44 critical minerals in 2024, including 14 rare earth lanthanides.
This dominance underpins China’s comparative advantage and strengthens its hand in trade negotiations with the United States.
China’s competitive edge in technology and innovation is also expanding. Its firms are steadily developing and patenting advanced products, maintaining a strong position in 5G, electric-vehicle batteries and artificial intelligence (AI).
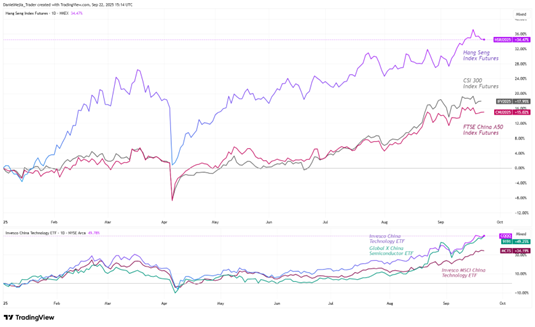
As a result, ETFs focused on Chinese technology firms have delivered strong year-to-date returns. These include the Invesco China Technology ETF (+50%), the Global X China Semiconductor ETF (+49%) and the Invesco MSCI China Technology ETF (+34%).
CPI remains the weakest link, but rising GDP and resilient services point to recovery