Dollar index climbs on strong economic data; Fed minutes show split
The US dollar index appreciated significantly, bolstered by robust economic data across the production, consumption, and real estate sectors, suggesting a more resilient long-term economic outlook. Simultaneously, the recently released Federal Reserve minutes revealed a notable divergence within the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).

The DXY index rose following positive reports on building permits, housing starts, and industrial production; furthermore, the decline in durable goods orders was less severe than market forecasts.
Federal Reserve minutes highlighted a split between members seeking to initiate rate cuts and those maintaining a restrictive stance to combat persistent inflationary pressures.
The UK inflation rate decelerated from 3.4% to 3.0%, providing the Bank of England (BoE) with greater justification for a potential shift toward a more dovish monetary policy.
Japan’s exports surged by approximately 17% year-on-year in January, reaching their highest level since late 2022, driven by strong demand across Asia, the European Union, and Australia.
DXY increases Amid strong economic data
The US dollar index (DXY) appreciated by 0.64% to 97.73 points following a series of robust economic releases. According to data from the Census Bureau, building permits rose by 4.3% after two months of contraction. Concurrently, housing starts increased by 6.2% in the latest reading, marking the highest level since March 2025. Both indicators signal a significant improvement in the long-term economic outlook, as real estate developers commit substantial capital to new projects. Conversely, while durable goods orders decreased by 1.4% month-on-month, the figure was more favourable than the 2% contraction anticipated by analysts.
Furthermore, Federal Reserve data indicated that industrial production accelerated from 1.3% to 2.3% in the most recent reading. This improvement was supported by a 0.7% monthly increase, surpassing the consensus estimate of 0.4%. In summary, these releases demonstrate a broader economic performance that has consistently exceeded analyst forecasts.
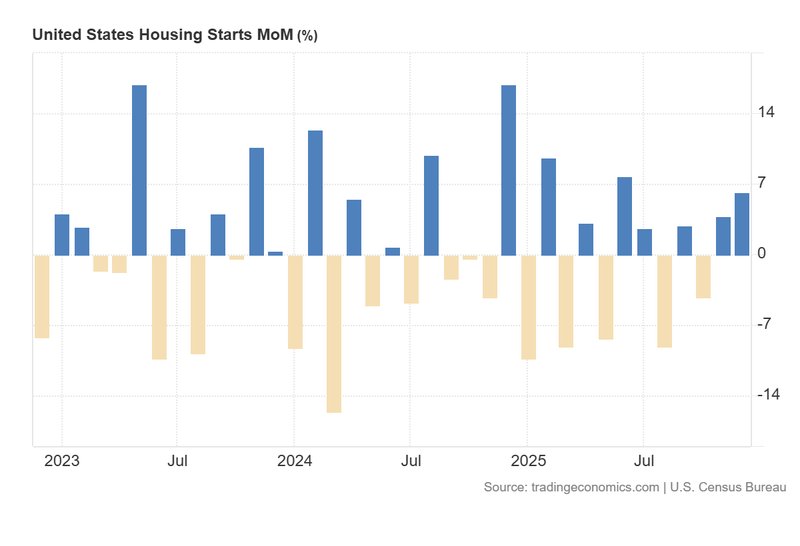
Figure 1. United States Housing Starts (2023–2025). Source: Data from the US Census Bureau; Figure obtained from Trading Economics.
Fed minutes exhibit uncertainty regarding future interest rate decisions
The minutes of the most recent Federal Reserve meeting, published today, confirmed a unanimous agreement to maintain interest rates at the 3.75% level. However, the document revealed significant internal divisions regarding the future path of monetary policy. Some participants expressed a willingness to raise rates should inflation remain at elevated levels, while others advocated for further cuts if inflation continues its trajectory toward the 2% target. This contrast in perspectives suggests that the Fed is transitioning toward a more neutral, albeit uncertain, stance.
The minutes also indicated that FOMC members are closely monitoring the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on productivity and market valuations. As reported by Reuters, some participants anticipate that AI-driven productivity gains could increase the supply of products and services, thereby exerting downward pressure on inflation. Conversely, members highlighted risks within financial markets, noting that AI-driven optimism has pushed valuations to elevated levels, potentially setting the stage for a significant stock market correction.
UK inflation decelerates in line with analyst expectations
Data from the UK Office for National Statistics (ONS) showed that the inflation rate decelerated from 3.4% in December to 3.0% in January, matching analyst forecasts. Core inflation—which excludes volatile food and energy prices—similarly eased from 3.2% to 3.1%. These figures, combined with recent labour market data showing an uptick in the unemployment rate, suggest that the Bank of England (BoE) has increasing grounds to consider interest rate reductions during the current year.
In response, the British pound fell by 0.55% to 1.3490 against the US dollar as market participants began to price in a higher probability of BoE rate cuts. Conversely, the FTSE 100 index rose by 1.23% to reach a new record high of 10,686, driven by investor optimism that a lower interest rate environment will support corporate growth through improved financing conditions.
Japanese exports increase predominantly while imports decline slightly
According to the Japanese Ministry of Finance, exports surged by 16.8% year-on-year in January, significantly exceeding the 12% increase anticipated by analysts. This represents the fastest pace of growth since December 2022. Information from Trading Economics attributes this improvement to a sharp rise in sales to Asia (specifically China, Taiwan, South Korea, Vietnam, and India), the European Union (notably Germany), Australia, and Russia. However, exports to the United States saw a slight decline, as implemented tariffs began to weigh on bilateral trade. In contrast, Japanese imports fell by 2.5% during the same period, compared to the 3% increase forecast by the market.
Despite the positive trade data, the Japanese yen depreciated by 0.92% to 154.71 against the US dollar, caught in the wake of the dollar’s broad recovery. Meanwhile, the Nikkei 225 appreciated by 0.82% to close at 57,617 points, reflecting positive expectations for the private sector.
