What is the difference between CFDs and futures
A contract for differences (CFD) is a financial agreement where investors exchange the difference in values of an asset when the contract opens and closes, Futures contracts are standardized agreements used to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a future date, traded on regulated exchanges.

CFD is a derivative contract between a trader and a broker. Instead of owning the underlying asset.
Futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell an asset at a fixed price on a specific future date.
CFDs are easier to access and require less capital to start trading, Futures require higher initial capital and can trigger faster margin calls.
What is a contract for differences (CFD)
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are one of the most widely used trading instruments in modern financial markets, especially for short-term traders and investors looking for flexibility. Despite their popularity, CFDs are often misunderstood.
At its core, a CFD is a derivative contract between a trader and a broker. Instead of owning the underlying asset, the trader agrees to exchange the difference in price of an asset between the time the trade is opened and when it is closed.
If the price moves in your favor, you profit. If it moves against you, you incur a loss. Ownership of the actual asset never changes hands.
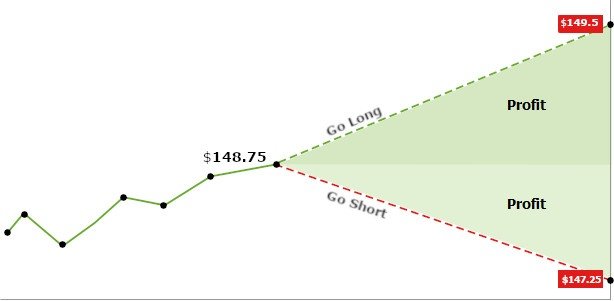
How CFD trading works
CFD trading is simple in structure but requires strong risk management, if you expect prices to rise you open buy (long), if you expect prices to fall you open sell position (short)
Profit or loss is calculated based on price movement × position size
Trades can be opened and closed quickly, making CFDs popular for short-term strategies
CFDs are leveraged instruments, meaning traders only need to deposit a fraction of the full position value. While leverage increases potential returns, it also magnifies losses.
Why traders use CFDs
Ability to trade rising and falling markets, access to multiple asset classes from one platform, lower capital requirements due to leverage, no ownership-related costs like stamp duty (in some regions)
However, CFDs are not suitable for all investors, especially those with low risk tolerance or long-term investment horizons.
Risks to know before trading CFDs
CFDs carry higher risk due to leverage. A small market move can result in a significant loss. Poor risk management, over-leveraging, or emotional trading can quickly erode capital.
This makes education, discipline, and position sizing essential.
What is a futures contract
A futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell an asset at a fixed price on a specific future date. These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges and are widely used for hedging risk and speculating on price movements.
Unlike CFDs trading, futures lock in a price today for delivery or settlement later.
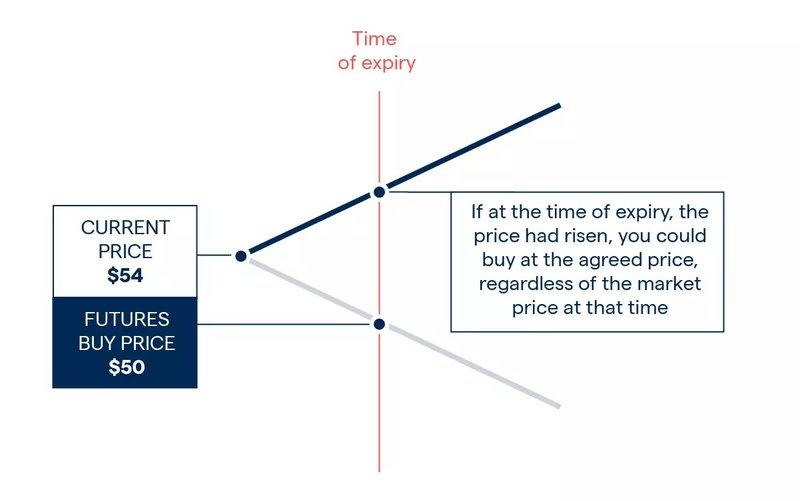
How futures trading works
Futures trading is based on agreements, not ownership.
When you enter a futures trade, you agree to buy or sell an asset at a fixed price on a future date. Traders can open buy positions (Long) if they expect prices to rise and open sell positions (Short) if they expect prices to fall.
You do not pay the full contract value. Instead, you post margin, a small percentage of the contract’s value.
Positions are marked to market daily, meaning profits and losses are settled each day. If losses reduce your margin below required levels, you must add funds or risk liquidation.
Most traders exit before expiration, avoiding physical delivery.
Why traders use futures
Hedging Businesses and institutions use futures to lock in prices. Airlines hedge fuel costs, farmers hedge crop prices, funds hedge equity exposure
Transparency, prices are formed on regulated exchanges, not by brokers.
Ability to short easily, selling futures is as simple as buying.
What is the difference between CFDs and futures
A CFD is a private contract between you and a broker. You are not trading on an exchange, and you never own the asset. You simply agree to exchange the price difference between the opening and closing of a trade, A futures contract is a standardized agreement traded on a regulated exchange. You agree to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a specific future date.
Trading costs
CFD trading costs are primarily determined by the broker. Traders pay a spread on each position, which represents the difference between the buy and sell price. In addition, holding CFD positions overnight usually incurs financing or swap fees, which accumulate the longer a trade remains open. Some brokers may also charge inactivity or administrative fees. As a result, CFD trading tends to become more expensive over time, especially for longer-term positions.
Futures trading costs are more transparent and standardized. Traders typically pay a fixed commission to their broker, along with exchange and clearing fees set by the futures exchange. Unlike CFDs, futures contracts do not carry overnight financing charges. Because of this structure, futures are often more cost-efficient for active traders or those holding positions for longer periods.
Leverage and margin
CFDs generally offer higher leverage, although the exact level depends on regulatory limits and broker policies. Margin requirements are set by the broker, not the market itself, which means leverage can amplify both gains and losses quickly. If risk is not carefully managed, losses can accumulate rapidly due to the ease of accessing high leverage.
Futures use exchange-defined margin requirements, which are standardized and transparent. While leverage in futures is typically lower than in CFDs, positions are marked to market daily. This means profits and losses are settled each day, reducing the buildup of hidden risk but requiring traders to maintain strict margin discipline.
Expiration and rollover
CFDs do not have an expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely as long as margin requirements are met and financing costs are paid. This flexibility makes CFDs suitable for open-ended strategies but increases the cost of long-term positions.
Futures contracts have fixed expiration dates. Traders must either close their positions before expiration or roll them into the next contract month. This structure makes futures more suitable for planned trades with defined time horizons rather than indefinite holding periods.
Regulation and transparency
CFDs are regulated at the broker level, meaning pricing, execution quality, and risk management depend heavily on the broker’s integrity. Because CFDs are over-the-counter products, there is a potential conflict of interest between the trader and the broker.
Futures are traded on centralized exchanges with strict regulatory oversight. Pricing is fully transparent, execution is standardized, and all participants trade under the same market conditions. This level of transparency is one of the most important distinctions between futures and CFDs.
Risk profile
CFDs are easier to access and require less capital to start trading, but their higher leverage significantly increases risk. Financing costs can also erode profitability over time, particularly in volatile or sideways markets.
Futures require higher initial capital and can trigger faster margin calls during sharp market moves. There is no protection from volatility, and price swings can be aggressive. While both instruments carry substantial risk, futures expose traders more directly to real market dynamics rather than broker-managed pricing.
FQAs
What is a CFD?
A CFD lets you trade price movements without owning the asset. You profit or loss from price changes only.
What is a futures contract?
A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a future date.
What is the main difference between CFDs and futures?
CFDs are broker-based and don’t expire, while futures trade on exchanges and have fixed expiration dates.
Which is more transparent: CFDs or futures?
Futures are more transparent because they trade on regulated exchanges.
Which is better for beginners?
CFDs are easier to access, while futures require more experience and discipline.