What Is the Smart Money Concept (SMC) in Forex—and How Can You Use It?
Smart Money Concept (SMC) is a modern price-action framework that decodes how banks, hedge funds, and liquidity providers—collectively “smart money”—move the market. By tracking institutional footprints such as order blocks, liquidity sweeps, and fair-value gaps, retail traders can shadow the big players instead of fighting them.
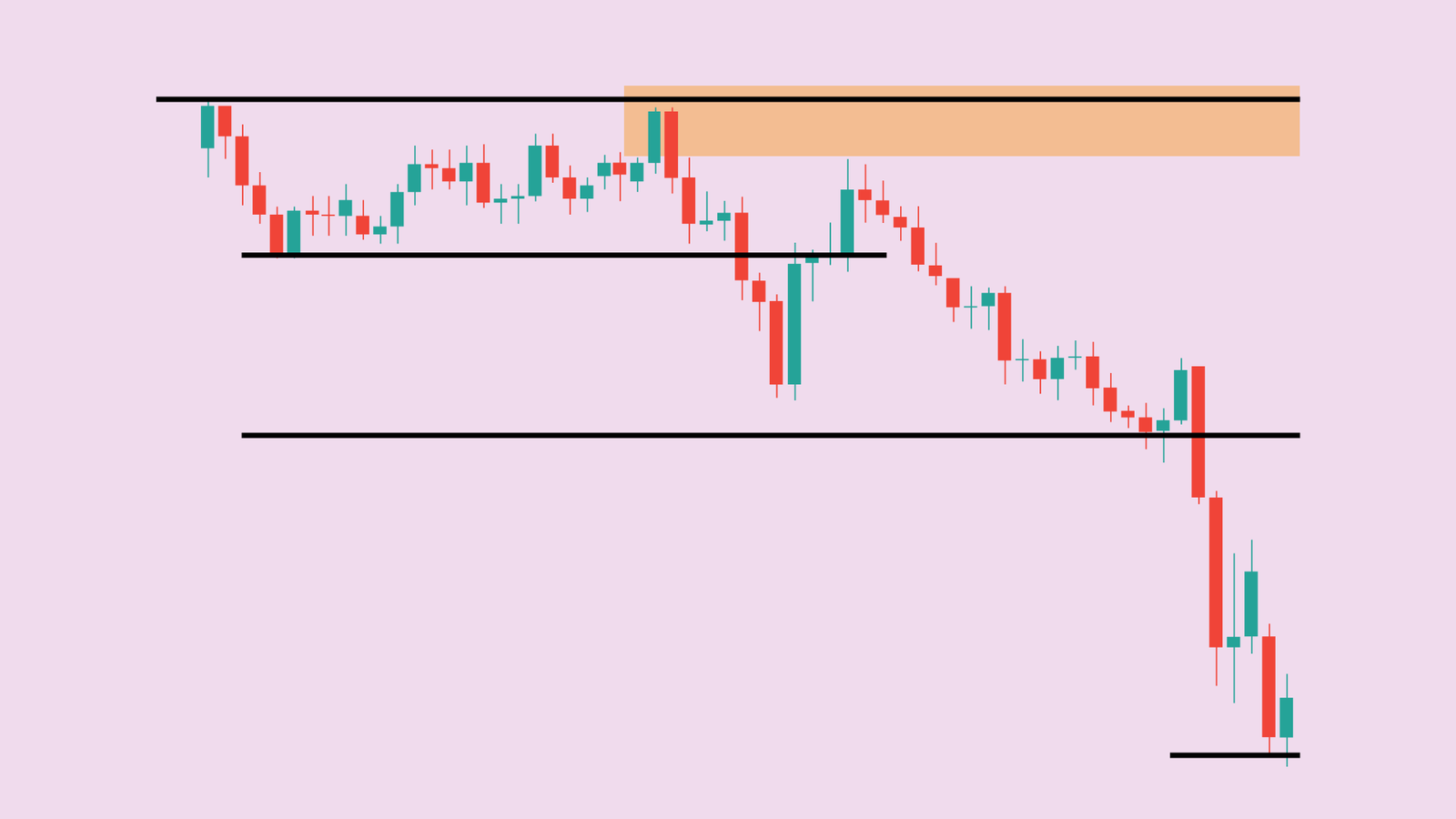
SMC was popularised by the Inner Circle Trader (ICT) community and focuses on institutional order-flow rather than retail indicators.
Core tools include market-structure shifts (MSS), liquidity pools, order blocks (OB), and fair-value gaps (FVG).
A valid bullish order block is the final down candle before an impulsive rally; price often revisits that zone for low-risk entries
Traders combine a top-down bias, liquidity logic, and strict risk limits to turn SMC theory into a practical edge.
The core idea: follow the money that moves the market
Large institutions cannot enter or exit multi-million-dollar positions with a single click; they break orders into chunks, engineer short-term fake-outs, and use liquidity pockets to fill size. SMC traders study those tell-tale patterns—especially sudden breaks of structure and rapid “displacement” candles—to infer where smart money is accumulating or distributing. The concept gained traction after ICT videos framed these patterns as the real supply-demand forces behind every chart.
Market-structure shift (MSS): the first clue that control is changing
A market in a down-trend prints lower highs and lower lows until, suddenly, a bullish displacement punches through the most recent lower high and closes with authority. That candle marks an MSS: smart money just flipped the script. SMC traders now watch for a pullback into the origin of the move—usually an order block or fair-value gap—before joining the new direction.
Order blocks: the launchpads of institutional moves
An order block is the last bearish candle (for longs) or bullish candle (for shorts) that precedes an explosive move. It represents unfinished institutional business; price often returns to “rebalance” remaining orders. A bullish EUR/USD order block at 1.0820-1.0835, for instance, becomes a magnet; if price revisits the zone on light volume, SMC traders look for a small reversal candle to enter with stops just beyond the block.
Liquidity pools and sweeps: why breaks often fake
Smart money seeks liquidity resting above obvious highs and below clean lows—the very places retail traders park stops. A quick spike that grabs those stops, then snaps back, is a liquidity sweep. In SMC logic, that sweep clears the path for price to travel the opposite way because opposing orders are now out of the way. Mapping equal highs, round numbers and session extremes helps traders anticipate where sweeps may occur.
Fair-value gaps: the price voids that beg to be filled
When a displacement candle kicks off a new leg, the middle of that candle often shows little to no trading—creating an imbalance known as a fair-value gap (FVG). Price statistically returns to such gaps about 70 % of the time, offering precise pullback zones. Bullish gaps are called BISI (buy-side imbalance, sell-side inefficiency); bearish gaps are SIBI. SMC traders align FVGs with order blocks for confluence.
A structured SMC trade routine
First, scan the daily chart and mark the most recent market-structure break; decide if bias is up or down. Second, drop to the four-hour chart and flag the nearest untested order block that sits in line with bias. Third, refine on the 15-minute: wait for a liquidity sweep into that block plus a tiny bullish or bearish confirmation candle. Risk no more than one percent of equity, place the stop just beyond the block’s extreme, and target the next opposing liquidity pool or FVG for a two-to-three-to-one reward profile.
Advantages—and real-world caveats
SMC offers microscopic precision and a narrative that explains why price wicks beyond resistance before it tanks. Its rules adapt across forex, indices, crypto, even commodities without parameter curve-fitting. The flip side is subjectivity: mis-labelling an order block or MSS can turn a high-probability setup into a costly fade. Beginners often clutter charts with every block and gap; disciplined filtering—trading only the clearest structures on liquid pairs during active sessions—solves most of those issues.
Risk management: the non-negotiable pillar
Because SMC levels are obvious to many traders, stop-hunts remain common. Professional SMC practitioners:
- keep risk below 1 % per trade;
- reduce size ahead of macro news;
- trail stops behind fresh order blocks once in profit;
- log every trade to refine their read of valid vs. failed structures.
With that discipline, even a 45 % win rate can be profitable because average wins (2 R–3 R) outweigh controlled losses.
FAQs
Does SMC replace traditional indicators?
Many traders drop lagging tools entirely; others keep a moving average for directional context. Price and liquidity always lead.
Which time frames work best?
Daily for bias, four-hour for levels, 15-minute or five-minute for entries. Scalpers can shrink that stack but should keep the top-down logic.